Faculty

Design of Advanced Knowledge
WATANABE Masataka
- Position
- Assoc. Prof.
- Affiliation
- Department of Systems Innovation, Faculty of Engineering, The University of Tokyo
- Keyword
- consciousness, machine consciousness, spiking neural networks, brain-machine-interface, mind-uploading
- watanabe(at)sys.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp※Please replace (at) with @ and send mail.
Unraveling the Neural Mechanism of Consciousness via Development of Machine Consciousness
 Research and Development of Machine Consciousness
Research and Development of Machine Consciousness
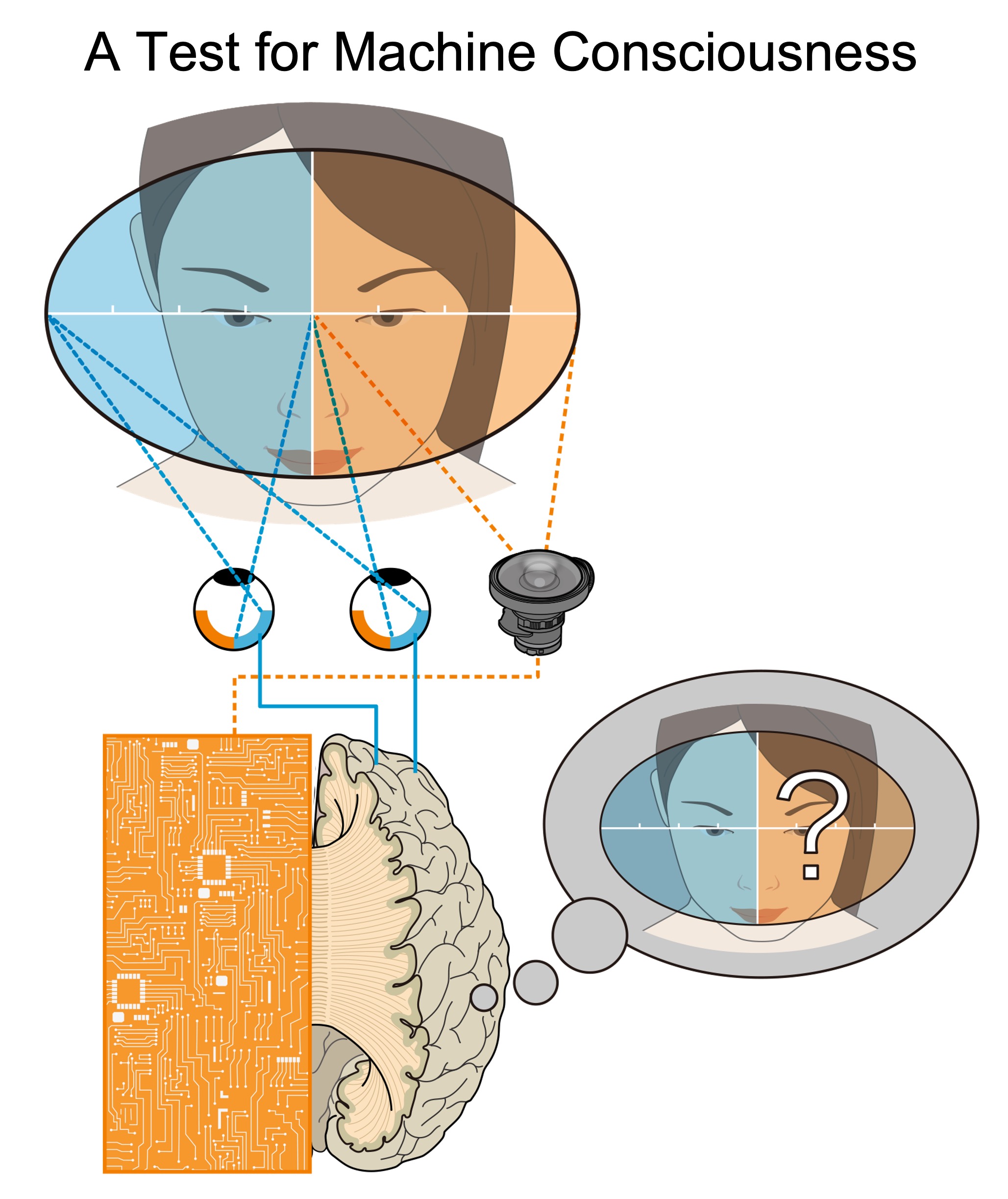 A Test for Machine Consciousness: integration of biological and artificial brain hemispheres
A Test for Machine Consciousness: integration of biological and artificial brain hemispheres
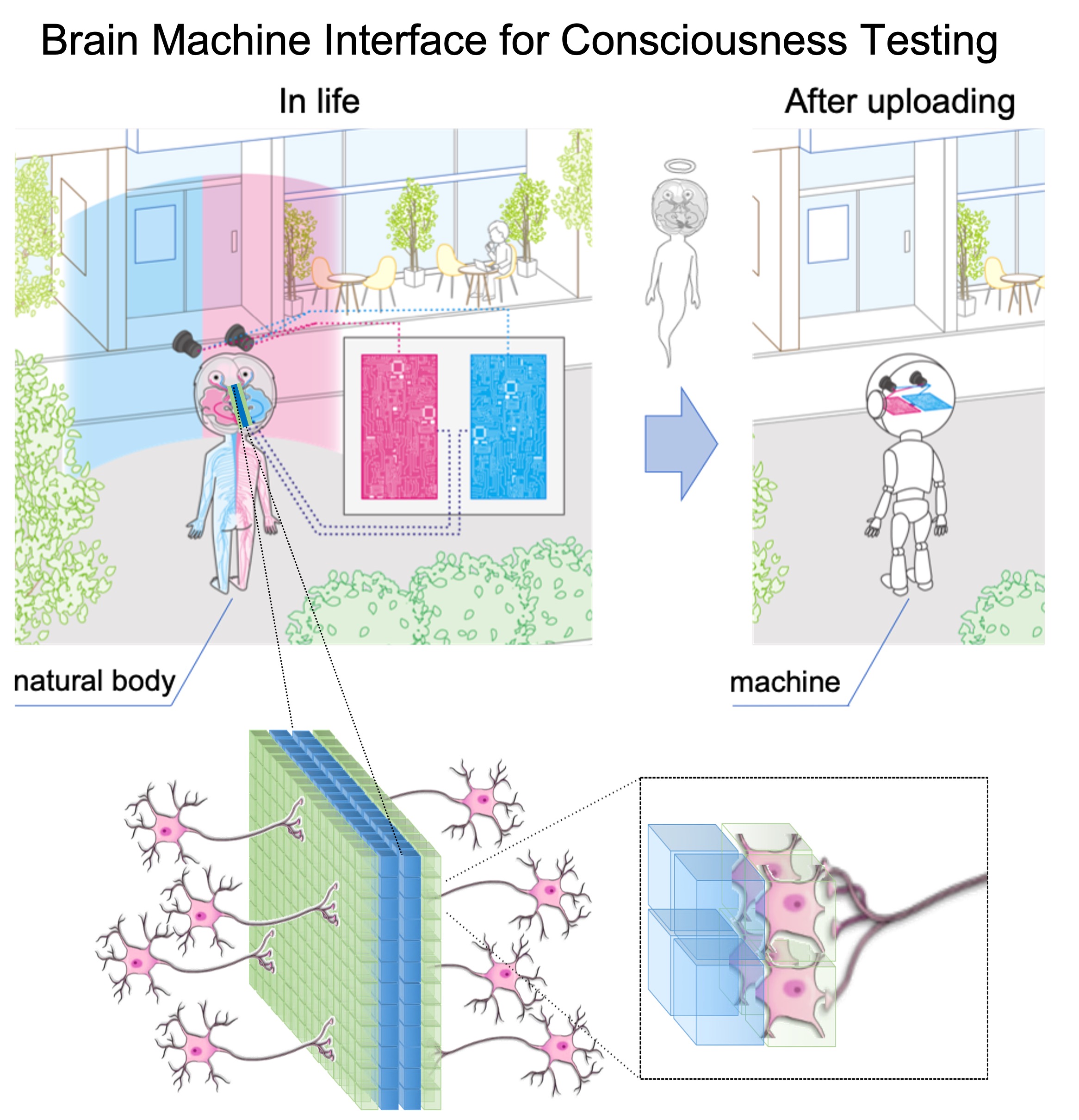 A Radically New Type of Brain-Machine Interface that Reads and Writes from Axonal Bundle Sections
A Radically New Type of Brain-Machine Interface that Reads and Writes from Axonal Bundle Sections
Research and Development of Machine Consciousness
Develop a large-scale spiking neural network as a candidate system of machine consciousness (see “From Biological to Artificial Consciousness” Springer). ① Apply discrete synaptic connections obtained from invasive connectome projects as initial synaptic weights ② As a working hypothesis, determine the system architecture (e.g. generative model) and train the network according to the loss functions defined by it ③ Validate the final product with objective measures such as functional properties (e.g. visual recognition) and network dynamics (e.g. similarity to noisy neural dynamics observed in mammal brains)
A Test for Machine Consciousness: integration of biological and artificial brain hemispheres
Since it is impossible to test machine consciousness through external observation or investigation of internal mechanisms using objective measures, only one method remains: making use of subjectivity. We need to connect our own brains to the above machine and “see” for ourselves whether consciousness resides within. By taking advantage of the “master-master” configuration of visual consciousness in biological cortical hemispheres, we replace one of our hemispheres with an artificial hemisphere. If we subjectively experience the machine visual field, we must conclude that a stream of visual consciousness has genuinely emerged in the artificial hemisphere as a “master”, and has been integrated to ours.
A Radically New Type of Brain-Machine Interface that Reads and Writes from Axonal Bundle Sections
The key to the above test is a new type of BMI that enables reading and writing information with unprecedented precision. The proposed BMI dissects axonal fibers that connect the two cortical hemispheres and inserts a CMOS based, double-sided two-dimensional electrode array (see “From Biological to Artificial Consciousness” Springer). This design allows independent reading and writing of all axonal projections that connects the two hemispheres. Importantly, due to the critical problems suggested by Histed et al. (Neuron, 2009), the proposed brain–machine interface is likely the only plausible method for biological brains to sufficiently communicate with artificial devices, leading to medical applications such as AI assistance and replacement of neuronal function.





